Common Causes of Joint Pain and How to Manage It Effectively

Understanding Joint Pain and Its Impact
Joint pain is a common issue affecting millions of people, from young athletes to older adults. It can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain that affects daily activities. Whether you’re dealing with stiffness, inflammation, or swelling, joint pain can limit mobility and diminish your quality of life. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 1 in 5 adults experience joint pain, with osteoarthritis being the leading cause.
Joint pain can result from a variety of causes, including injury, overuse, or underlying conditions such as arthritis. Understanding the root cause of your joint pain is the first step in managing it effectively.
What are Common Causes of Joint Pain?
Joint pain can stem from multiple sources, some of which are temporary, while others may require long-term management. Below are some of the most common causes:
- Osteoarthritis
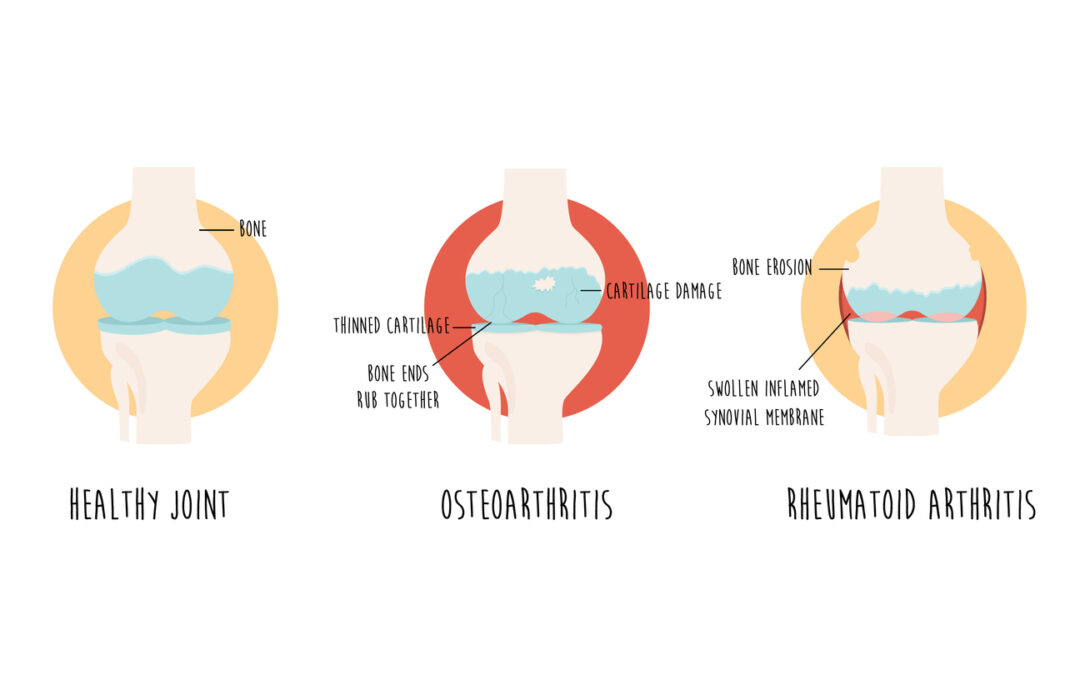
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis and occurs when the cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time. It typically affects weight-bearing joints, such as the knees, hips, and spine, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Osteoarthritis becomes more prevalent as people age and is one of the leading causes of joint pain in older adults.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune condition that causes the immune system to attack the synovium, the lining of the joints. This leads to inflammation, pain, and eventual joint damage. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is related to wear and tear, rheumatoid arthritis can affect people at any age and tends to affect multiple joints simultaneously.
- Injury or Trauma
Joint injuries are common among athletes and active individuals. Sprains, strains, and fractures can damage the structures in and around the joint, causing pain, swelling, and inflammation. Sports that involve repetitive motion or high-impact activities, such as running, tennis, and basketball, increase the risk of joint injuries.
- Tendonitis
Tendonitis occurs when the tendons, which connect muscle to bone, become inflamed due to overuse. This is particularly common in joints like the shoulders, elbows, and knees, and is often seen in athletes or people who perform repetitive movements in their work. Conditions like tennis elbow and jumper’s knee are examples of tendonitis.
- Gout
Gout is a form of arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals build up in the joints, causing sudden and severe pain, often in the big toe. Gout attacks can come on quickly and are known for being extremely painful. Risk factors for gout include a diet high in purines (found in red meat and shellfish), obesity, and certain medications.
- Bursitis
Bursitis happens when the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints, become inflamed. Bursitis often affects the hips, elbows, and shoulders and is commonly caused by repetitive motion or prolonged pressure on the joint. People who spend long periods kneeling or leaning on their elbows may develop bursitis over time.
What are Effective Strategies for Managing Joint Pain?
If you are dealing with joint pain, there are several strategies to help alleviate discomfort, improve mobility, and prevent further damage. Below are some evidence-based management techniques recommended by orthopedic specialists.
- Rest and Activity Modification
For joint pain related to injury or overuse, rest is essential for allowing the affected joint to heal. However, complete inactivity can sometimes worsen stiffness and weaken surrounding muscles. It’s important to strike a balance by modifying your activities. For example, switching from high-impact sports like running to low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling can reduce joint strain while keeping you active.
- Physical Therapy and Exercise
Exercise is one of the most effective ways to manage chronic joint pain. Strengthening the muscles around the joint can provide better support and reduce stress on the joint itself. Physical therapy can also help improve flexibility and restore function. According to the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), low-impact exercises such as yoga, Pilates, and aquatic therapy are particularly beneficial for joint health.
- Medications
For temporary relief, over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, can help reduce pain and inflammation. In more severe cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications or suggest corticosteroid injections to provide longer-lasting relief. If the joint pain is related to rheumatoid arthritis or another autoimmune condition, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) or biologics may be recommended to control inflammation. Learn about how MCH can help treat your autoimmune conditions by scheduling an appointment with our Rheumatology clinic.
- Weight Management
Carrying excess weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints like the knees, hips, and spine. For every pound of body weight, your knees experience an additional four pounds of pressure. Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce joint pain and slow the progression of osteoarthritis. A study published in the Arthritis & Rheumatism Journal showed that even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can lead to significant improvements in joint pain.
- Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat can relax tight muscles and improve circulation around a sore joint, while cold therapy can reduce inflammation and numb the area, providing pain relief. Use a heating pad or warm compress for stiffness, and apply an ice pack for acute swelling or inflammation.
- Joint Injections
For more persistent joint pain that does not respond to medications or therapy, joint injections may provide relief. Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation in the joint and relieve pain for several weeks or months. In some cases, hyaluronic acid injections are used to lubricate the joint, especially in cases of osteoarthritis, to improve mobility and reduce pain.
How to Prevent of Joint Pain Long-Term
Preventing joint pain and maintaining healthy joints requires a proactive approach. Here are a few tips to protect your joints long-term:
- Stay Active: Regular movement is key to keeping your joints flexible and strong. Incorporate low-impact activities like swimming, walking, and cycling into your routine to reduce joint strain.
- Strengthen Surrounding Muscles: Building strong muscles around your joints, particularly in your core, legs, and hips, provides additional support and reduces the risk of injury.
- Use Proper Ergonomics: Ensure your workspace and daily habits support good posture and minimize joint strain. If you spend long hours at a desk, consider adjusting your chair and computer setup to promote neutral joint positioning.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce inflammation in the body and protect joint health. Avoid processed foods high in sugar and saturated fats, as they can worsen inflammation.
When to See a Specialist for Joint Pain
While mild joint pain can often be managed at home, there are times when you should consult a healthcare provider:
- The pain lasts for more than a few days or gets progressively worse.
- There is significant swelling, warmth, or redness around the joint.
- You experience sudden and severe pain, especially after an injury.
- You have difficulty moving the joint or bearing weight.
At Monadnock Community Hospital, Dr. McNamara specializes in diagnosing and treating joint pain. We offer personalized treatment plans designed to address the root cause of your pain and restore your mobility. If you’re experiencing joint pain, contact us today to schedule a consultation and explore your options for relief.
Resources:
For more detailed information on joint pain and management strategies, visit these trusted resources:

Why Choose Monadnock Orthopaedic Associates?
Our board-certified pain management specialists combine decades of experience with training from prestigious institutions like the Mayo Clinic. We offer comprehensive orthopedic care using advanced techniques and technology, all while providing personalized attention. At Monadnock Orthopaedic Associates, we’re committed to getting you back to pain-free living as quickly as possible with expert, compassionate care tailored to your unique needs. Choose us for expert care that’s close to home, where your well-being is our highest priority.
 Monadnock Orthopaedic Associates
Monadnock Orthopaedic Associates
Monadnock Community Hospital
Bond Wellness Center Suite 200
458 Old Street Road
Peterborough, NH 03458
Phone: 603-924-2144
Fax: 603-924-3993
Array
(
[section_title] =>
[section_text] =>
[posts_selection] => auto_taxonomy_terms
[section_posts] => Array
(
[0] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 39214
[post_author] => 9192204
[post_date] => 2024-12-16 08:26:06
[post_date_gmt] => 2024-12-16 13:26:06
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Safe Use of Opioids for Pain Management
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => safe-opioid-use-pain-management
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-09-10 15:36:22
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-09-10 19:36:22
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/common-causes-joint-pain-copy/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[1] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 39126
[post_author] => 9192204
[post_date] => 2024-10-28 07:23:34
[post_date_gmt] => 2024-10-28 11:23:34
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Common Causes of Joint Pain and How to Manage It Effectively
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => common-causes-joint-pain
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-08-22 17:31:44
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-08-22 21:31:44
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/effective-neck-pain-management-copy/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[2] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 39081
[post_author] => 9192204
[post_date] => 2024-09-18 18:10:52
[post_date_gmt] => 2024-09-18 22:10:52
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Video: Fitness for Life Seminar Video
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => fitness-for-life-seminar-video-2024
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-09-10 15:45:18
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-09-10 19:45:18
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/opioid-free-seminar-video-2024-copy/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[3] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 38946
[post_author] => 9192204
[post_date] => 2024-06-14 14:04:43
[post_date_gmt] => 2024-06-14 18:04:43
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Video: Unlocking Opioid-Free Pain Management Seminar Video
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => opioid-free-seminar-video-2024
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-09-10 15:45:29
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-09-10 19:45:29
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/opioid-free-seminar-video-2024-copy/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[4] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 37328
[post_author] => 9192204
[post_date] => 2024-06-10 08:51:41
[post_date_gmt] => 2024-06-10 12:51:41
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Effective Neck Pain Management Strategies: Reclaim Your Comfort and Mobility
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => effective-neck-pain-management
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-09-10 15:23:19
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-09-10 19:23:19
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/?p=37328
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[5] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 37373
[post_author] => 9192204
[post_date] => 2024-05-13 07:33:08
[post_date_gmt] => 2024-05-13 11:33:08
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Low Back Pain Management | Physical Therapy, Minimally Invasive & Surgical Options
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => lower-back-pain-management
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-09-10 15:34:38
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-09-10 19:34:38
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/?p=37373
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[6] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 37609
[post_author] => 9192204
[post_date] => 2024-04-29 13:24:35
[post_date_gmt] => 2024-04-29 17:24:35
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Provider Spotlight: Terrence McNamara - Your Trusted Physiatrist and Pain Management Specialist
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => dr-terrence-mcnamara-pain-management-specialist
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-09-10 15:36:13
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-09-10 19:36:13
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/dr-shawn-harrington-mch-orthopedic-surgeon-copy/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[7] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 37284
[post_author] => 9192204
[post_date] => 2024-02-09 11:26:19
[post_date_gmt] => 2024-02-09 16:26:19
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Managing Chronic Pain - Orthopedic Solutions and Lifestyle Changes
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => orthopedic-solutions-for-managing-chronic-pain
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-09-10 15:34:42
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-09-10 19:34:42
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/managing-chronic-pain-orthopedic-solutions-and-lifestyle-changes-copy/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[8] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 36942
[post_author] => 9192204
[post_date] => 2023-12-18 08:00:42
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-12-18 13:00:42
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Treatments for Pinched Nerves in Your Spine
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => treatments-for-pinched-nerves-in-your-spine
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-09-10 15:36:47
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-09-10 19:36:47
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/?p=36942
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[9] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 36732
[post_author] => 9192204
[post_date] => 2023-12-04 08:55:47
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-12-04 13:55:47
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Controlling Inflammation with Proper Nutrition for Orthopedics or Pain
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => harnessing-the-power-of-nutrition-for-inflammation-control
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-08-28 13:14:25
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-08-28 17:14:25
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/health-and-wellness-seminars-video-230817-copy-copy/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[10] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 37288
[post_author] => 9192204
[post_date] => 2023-10-13 12:01:31
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-10-13 16:01:31
[post_content] =>  Understanding Your Health is a free educational video series from Monadnock Community Hospital designed to inform, support, and empower our community. Each session features trusted healthcare professionals sharing expert insights on topics that matter most to your health and well-being. Whether you're looking to learn something new or take proactive steps toward a healthier lifestyle, you're in the right place.
Understanding Your Health is a free educational video series from Monadnock Community Hospital designed to inform, support, and empower our community. Each session features trusted healthcare professionals sharing expert insights on topics that matter most to your health and well-being. Whether you're looking to learn something new or take proactive steps toward a healthier lifestyle, you're in the right place.
Part of the Health & Wellness Seminars at Monadnock Community Hospital (MCH)
Common Shoulder Problems and At-Home Solutions Seminar
October 12, 2023 at Monadnock Community Hospital
Presenter: Dr. Shawn P. Harrington, MD, FAAPMR
Part of the Health & Wellness Seminars at Monadnock Community Hospital (MCH)
Dr. Harrington has been this community’s Physiatrist and Musculoskeletal Specialist at Monadnock Orthopaedic Associates for the past two decades. He will review common shoulder pains we all experience, some options for self-care, and reasons to seek medical consultation. This workshop is directed toward anyone with interest in or personal experience with shoulder pain, whether from wear-and-tear, an old injury, athletics, or aging. Interactive discussion is welcome.
Dr. Harrington’s practice as a board-certified Musculoskeletal Physician is grounded in thorough diagnostic evaluation and treatment with 20 years of experience. He seeks to define a problem and then offers options and choices to guide patients toward a course of treatment all parties can agree on, leading to the best possible outcome. Recognizing that not every first choice leads to success, he establishes plans with patients that help bring about their goals.
Learn more about Dr Shawn P Harrington
Learn more about Monadnock Orthopaedic Associates
 At Monadnock Community Hospital, we are dedicated to enhancing the health and well-being of our community. This seminar is just one way we strive to elevate the health of our community by providing accessible, high-quality care.
At Monadnock Community Hospital, we are dedicated to enhancing the health and well-being of our community. This seminar is just one way we strive to elevate the health of our community by providing accessible, high-quality care.
 Learn more about the Health and Wellness Seminars at MCH
Watch more videos of our seminars
Background audio: Ten Minutes of Ambient Piano Relaxation by Music_For_Videosfrom Pixabay
[post_title] => Video: Common Shoulder Problems and At-Home Solutions Seminar with Dr. Shawn P. Harrington 2023
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => common-shoulder-problems-and-at-home-solutions
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-09-10 15:45:13
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-09-10 19:45:13
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/health-and-wellness-seminars-video-231012-copy/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[11] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 38341
[post_author] => 9192204
[post_date] => 2023-05-15 09:23:49
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-05-15 13:23:49
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Heartfelt Stories - Renee Didn’t Deserve to Live in Pain
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => patient-stories-deschuiteneer-2022
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-09-16 12:06:16
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-09-16 16:06:16
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/?p=38341
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
)
[posts_limit] => 30
[post_type] => post
[taxonomy] => tag
[terms] => mcnamara, pain management
[section_id] => post-grid-13
)
Learn more about the Health and Wellness Seminars at MCH
Watch more videos of our seminars
Background audio: Ten Minutes of Ambient Piano Relaxation by Music_For_Videosfrom Pixabay
[post_title] => Video: Common Shoulder Problems and At-Home Solutions Seminar with Dr. Shawn P. Harrington 2023
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => common-shoulder-problems-and-at-home-solutions
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-09-10 15:45:13
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-09-10 19:45:13
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/health-and-wellness-seminars-video-231012-copy/
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[11] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 38341
[post_author] => 9192204
[post_date] => 2023-05-15 09:23:49
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-05-15 13:23:49
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Heartfelt Stories - Renee Didn’t Deserve to Live in Pain
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => patient-stories-deschuiteneer-2022
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2025-09-16 12:06:16
[post_modified_gmt] => 2025-09-16 16:06:16
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://monadnockcommunityhospital.com/?p=38341
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => post
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
)
[posts_limit] => 30
[post_type] => post
[taxonomy] => tag
[terms] => mcnamara, pain management
[section_id] => post-grid-13
)


 At Monadnock Community Hospital, we are dedicated to enhancing the health and well-being of our community. This seminar is just one way we strive to elevate the health of our community by providing accessible, high-quality care.
At Monadnock Community Hospital, we are dedicated to enhancing the health and well-being of our community. This seminar is just one way we strive to elevate the health of our community by providing accessible, high-quality care.
